rim lichen
Lecanora carpineaDescription 6
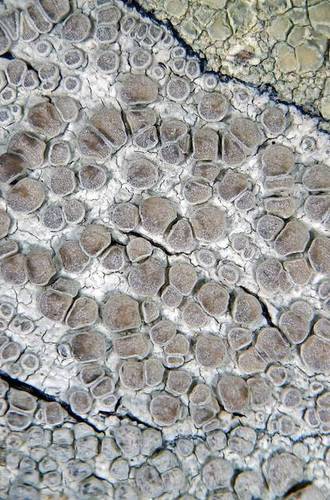
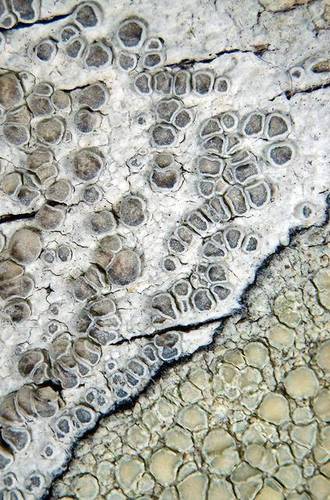
Thallus: crustose, continuous or rimose-areolate; prothallus: not visible, or white; areoles: flat, thin or thick, opaque, ecorticate; surface: whitish gray to gray or pale green to greenish white, smooth, epruinose, with an indistinct margin, esorediate; Apothecia: sessile, 0.5-1.3 mm in diam., lecanorine; disc: orange-brown or pale pink to carneous, plane or convex, heavily whitish gray pruinose; margin: concolorous with thallus, thin or thick, persistent, prominent, not flexuose, smooth, entire, without a parathecial ring; amphithecium: present, with numerous algal cells, with numerous small crystals which dissolve in K, 35-80 µm thick, corticate; cortex: hyaline or pale yellow, indistinct or distinct, basally not thickened, interspersed, (30-)55-75(-80) µm thick laterally, (30-)55-75(-80) µm thick basally; parathecium: hyaline, containing crystals insoluble in K; epihymenium: brown to dark brown, with pigment dissolving in K, with crystals dissolving in K; hymenium: clear; paraphyses: slightly thickened (up to 2.5 µm wide) apically, not pigmented; subhymenium: hyaline, 15-20 µm thick; hypothecium: hyaline, without oil droplets; asci: clavate, 8-spored; ascospores: hyaline, simple, ellipsoid or broadly ellipsoid, (9-)12-14(-14.5) x (5.5-)6-7.5(-8.5) µm; wall: less than 1 µm thick; Pycnidia: not seen; Spot tests: K+ yellow, C+ orange to orange-red, P- or P+ pale yellow; Secondary metabolites: atranorin (major), chloroatranorin (minor), eugenitol (minor), and sordidone (major).; Substrate and ecology: on bark or wood of deciduous trees and conifers; World distribution: temperate areas of Africa, Asia, New Zealand, Europe, and North America; Sonoran distribution: Arizona, southern California, and Chihuahua.; Notes: Lecanora carpinea is easily recognized by its heavily pruinose apothecial disc, a well developed amphithecial cortex and the presence of sordidone in the apothecial pruina. Very similar is the Eurasian L. leptyrodes that can be distinguished by the absence of a cortex. Some morphs of L. caesiorubella may be similar and some chemotypes also contain sordidone. However, this species is readily distinguished by the absence of an amphithecial cortex and the presence of depsidones.
Fuentes y créditos
- (c) Biopix, algunos derechos reservados (CC BY-NC), http://www.biopix.com/PhotosMedium/JCS%20Lecanora%20carpinea%2030491.jpg
- (c) Richard Droker, algunos derechos reservados (CC BY-SA), https://images.mushroomobserver.org/640/202144.jpg
- (c) Richard Droker, algunos derechos reservados (CC BY-SA), https://images.mushroomobserver.org/640/202145.jpg
- (c) James Lindsey, algunos derechos reservados (CC BY-SA), https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/7/76/Lecanora.carpinea2.-.lindsey.jpg
- (c) James Lindsey, algunos derechos reservados (CC BY-SA), https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/8/82/Lecanora.carpinea.-.lindsey.jpg
- (c) Lichen Unlimited: Arizona State University, Tempe., algunos derechos reservados (CC BY-NC-SA), http://eol.org/data_objects/10548343